Resolving “Windows NetBIOS / SMB Remote Host Information Disclosure” (2020)

Resolving “Windows NetBIOS / SMB Remote Host Information Disclosure” (2019)
Vulnerability scans and penetration tests will often produce a substantial number of issues such as “Windows NetBIOS / SMB Remote Host Information Disclosure”. This is an inherent byproduct of having workstations with NetBIOS enabled. On most modern networks NetBIOS can be disabled in favor of SMB over TCP, however, older networks may wish to leave this enabled and accept the risk of hostname disclosure.
Disabling NetBIOS
NetBIOS can be disabled via DHCP or explicitly configured in the network adapter. When configuring via DHCP the client system must also be configured to inherit these settings from the DHCP server. When remediating this vulnerability it is recommended that both the DHCP server and local systems are configured to disable NetBIOS. In Windows environments using a domain and GPO this can be implemented via GPO as well.
Only after being completely sure that this protocol is no longer used we can proceed to disable from our environment.
Remediation Overview
-
Option 1 – Disable NetBIOS via system configuration
- Disable NetBIOS in the network DHCP server
- Disable NetBIOS on local systems (Windows 10, Windows 2016 Server, Windows 2019 Server)
- Disable NetBIOS on local systems (Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 2000 Server, Windows 2003 Server, Windows 2008 Server and Windows 2012 Server)
-
Option 2 – Disable NetBIOS via GPO
-
Verify Remediation
Option 1 (part 1): Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP on Windows DHCP Server
-
Open DHCP Console:
-
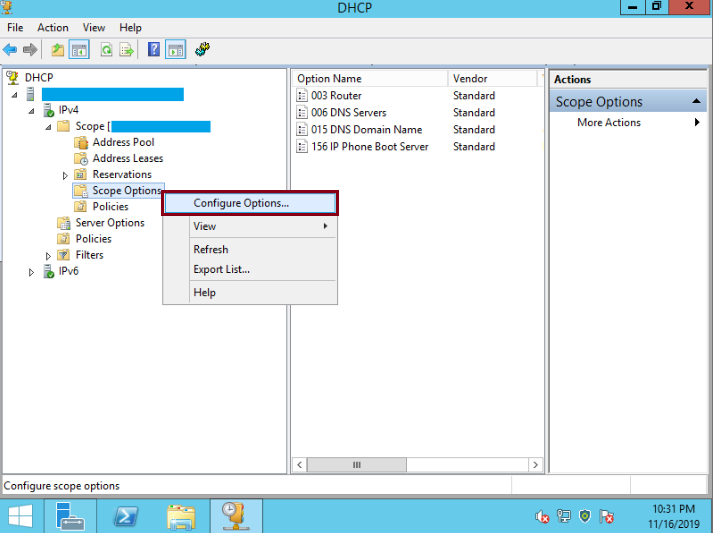
Once on DHCP Console go to the name of the server, IPv4, Scope, right click on Scope Options then, left click on Configure Options:
-
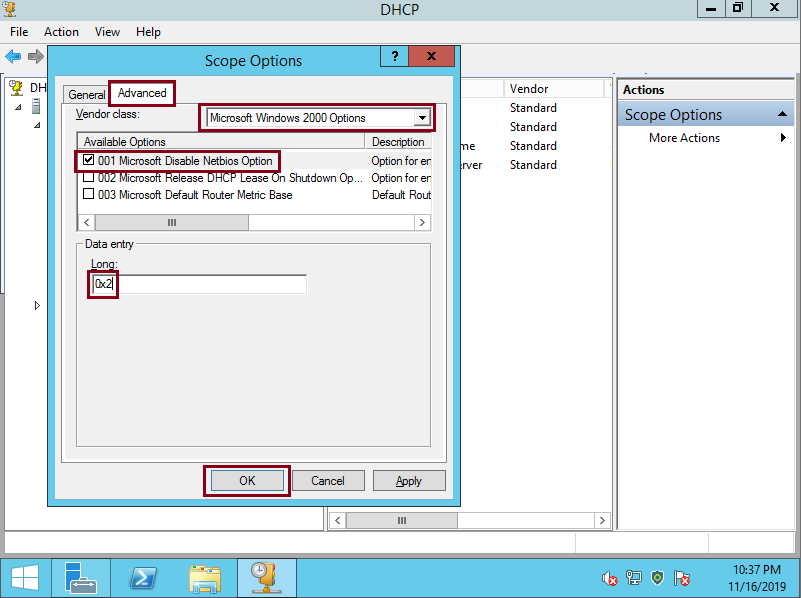
On Scope Options select the Advanced Tab, then, on Vendor class select Microsoft Windows 2000 Options, check the Microsoft Disable Netbios Option and on Long: Type 0x2, then click OK
-
DHCP clients will now be instructed to disable NetBIOS over TCP. We still must continue to part 2 to disable NetBIOS on individual systems.
Option 1 (part 2): Disabling NetBIOS over TCP/IP Manually on Windows 10, Windows 2016 Server, Windows 2019 Server
-
Click on the Windows Button and then on Settings:
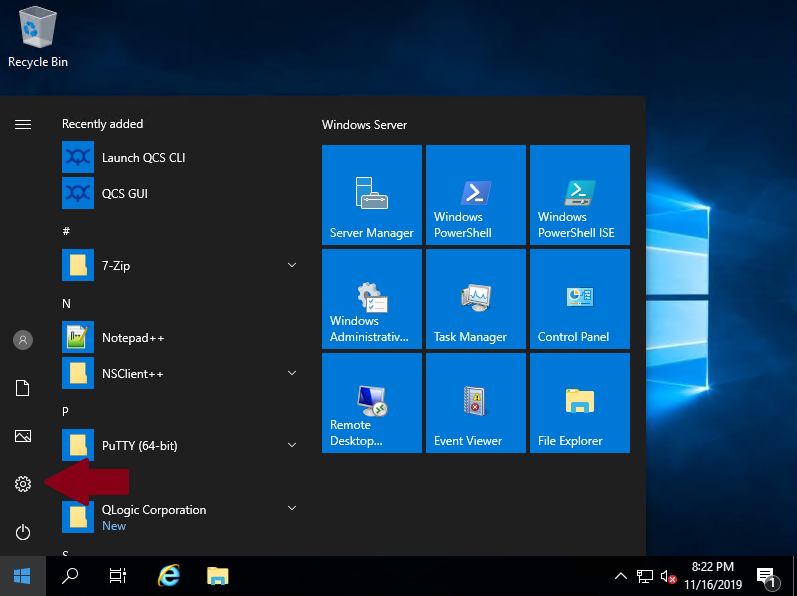
-
Click on Change adapter options:
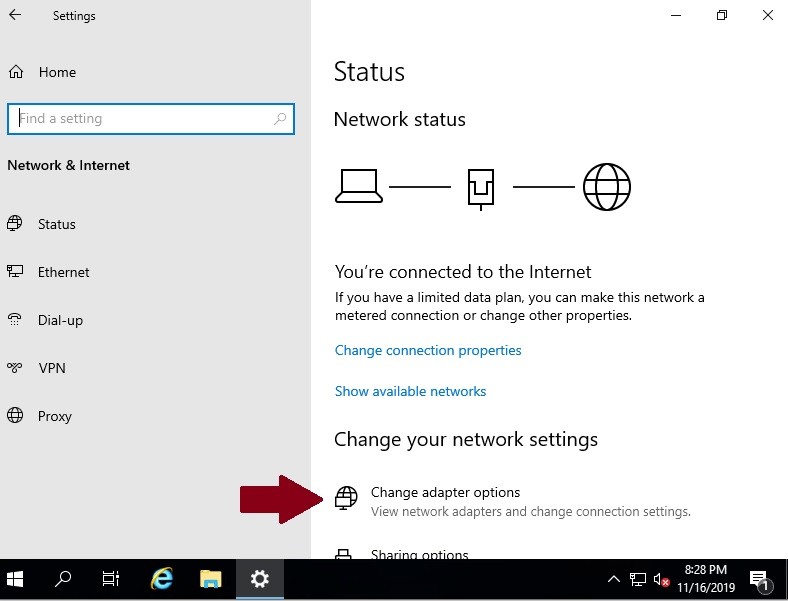
-
You should right click on the network adapter, and then left click on Properties
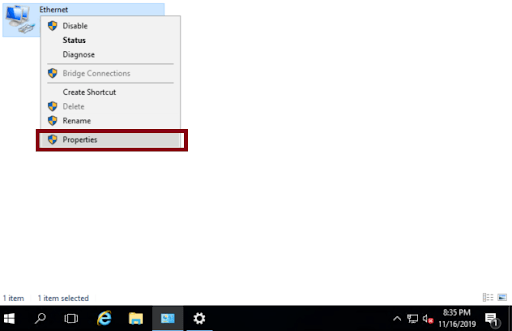
-
On Ethernet Properties you should select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then click on Properties
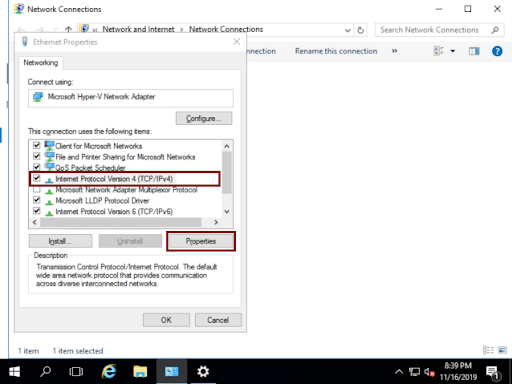
-
Click on Advanced
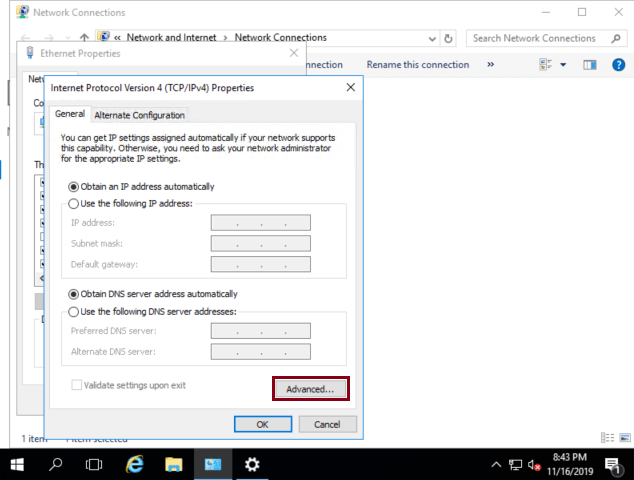
-
Click on WINS tab, check Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP and then click on OK
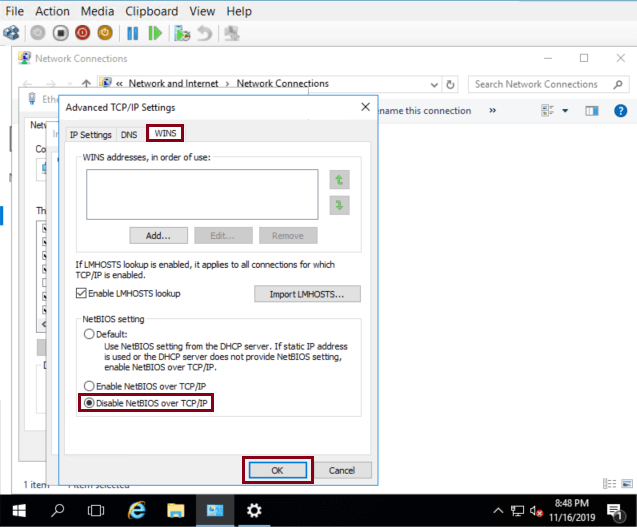
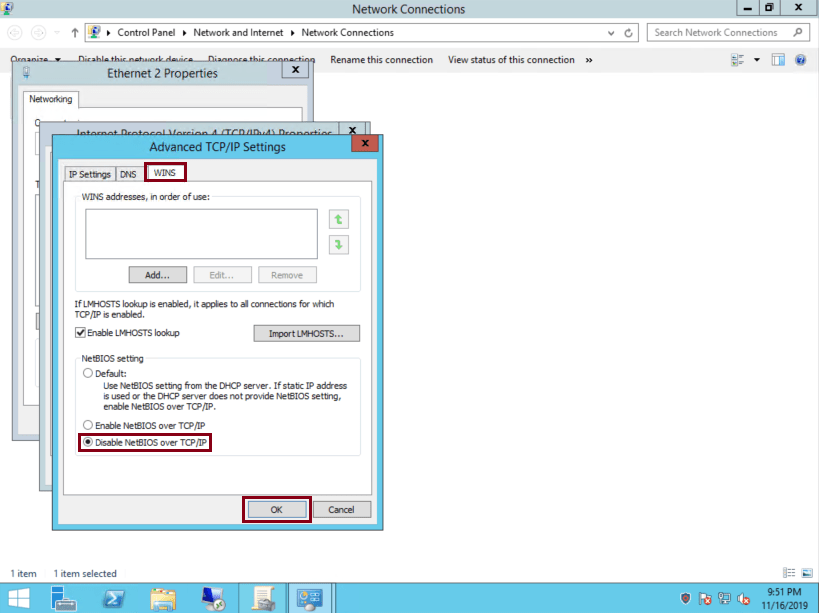
NetBIOS is now disabled.
Disabling NetBIOS over TCP/IP Manually on Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 2000 Server, Windows 2003 Server, Windows 2008 Server and Windows 2012 Server
- Open Control Panel:
Click ‘Network and Internet’: 2. 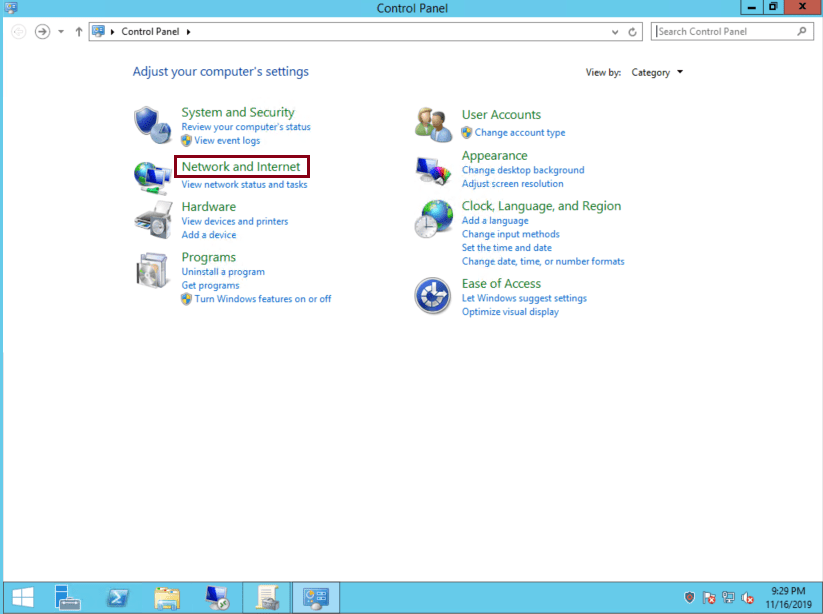
-
Click ‘Network and Sharing Center’:
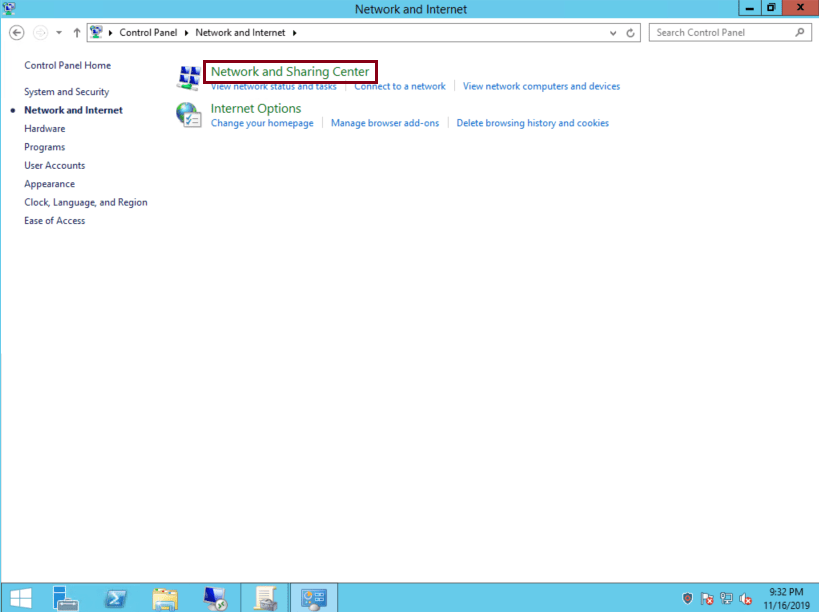
-
Click ‘Change adapter settings’:
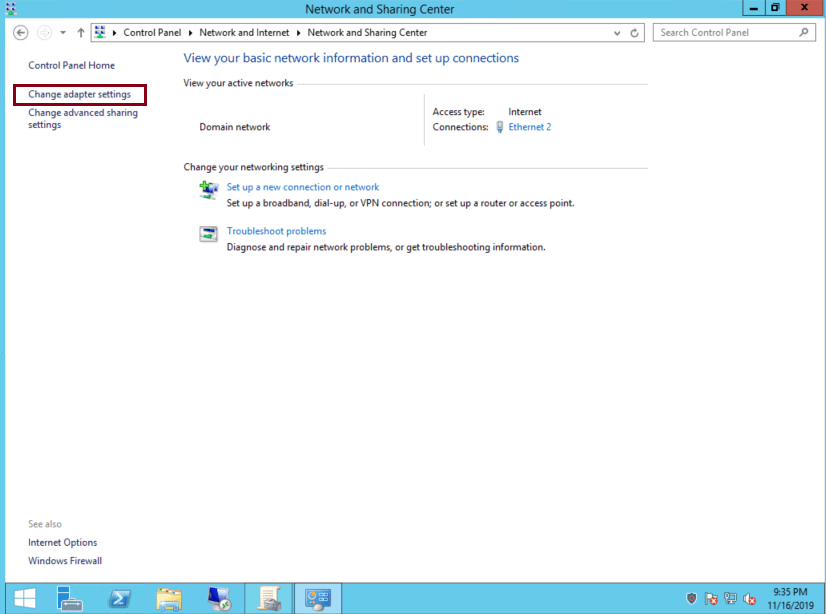
-
Click on the network adapter, and then left click on ‘Properties’:
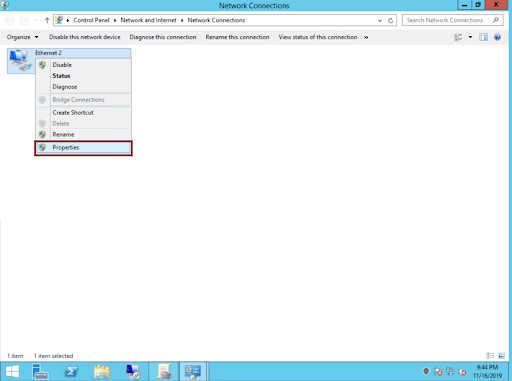
-
On Ethernet Properties select ‘Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)’ and then click on ‘Properties’:
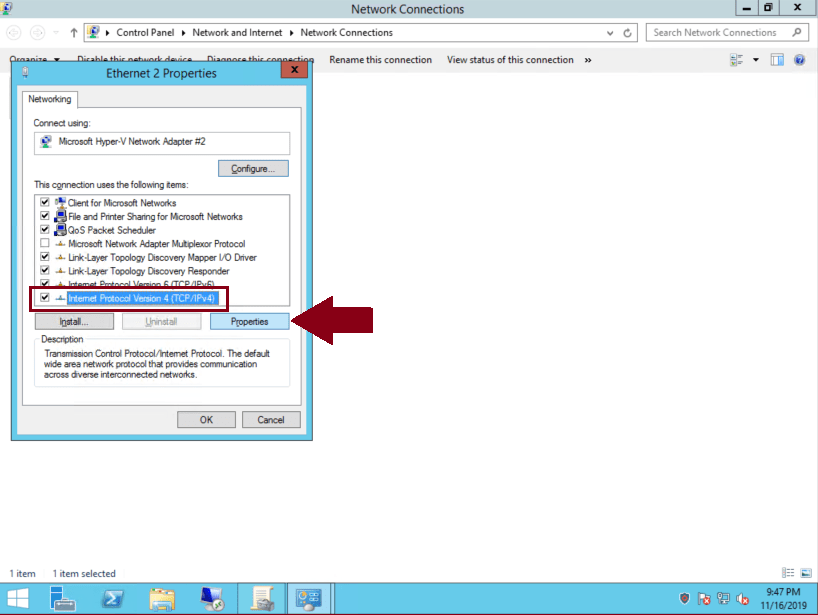
-
Click on ‘Advanced’:
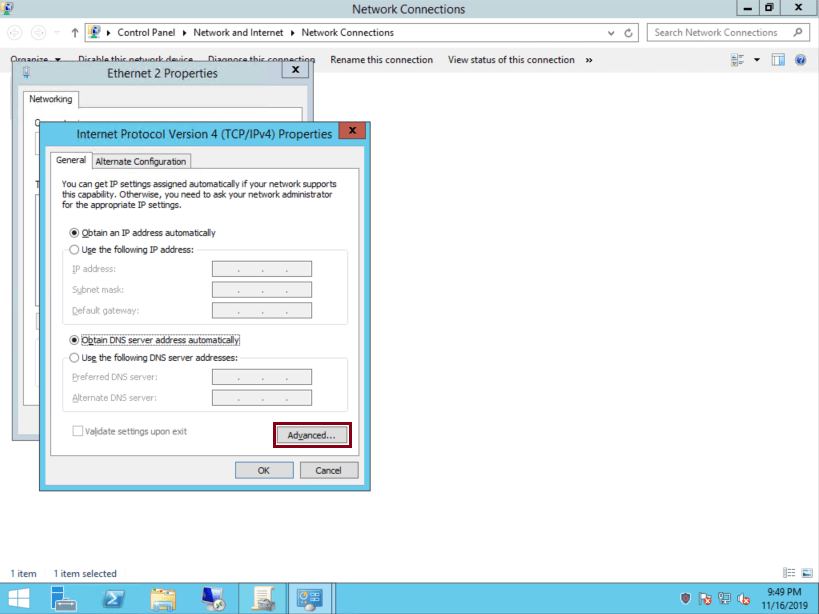
-
Click on ‘WINS’ tab, check ‘Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP’ and then click on ‘OK’:
Testing if NetBios over TCP/IP is disabled
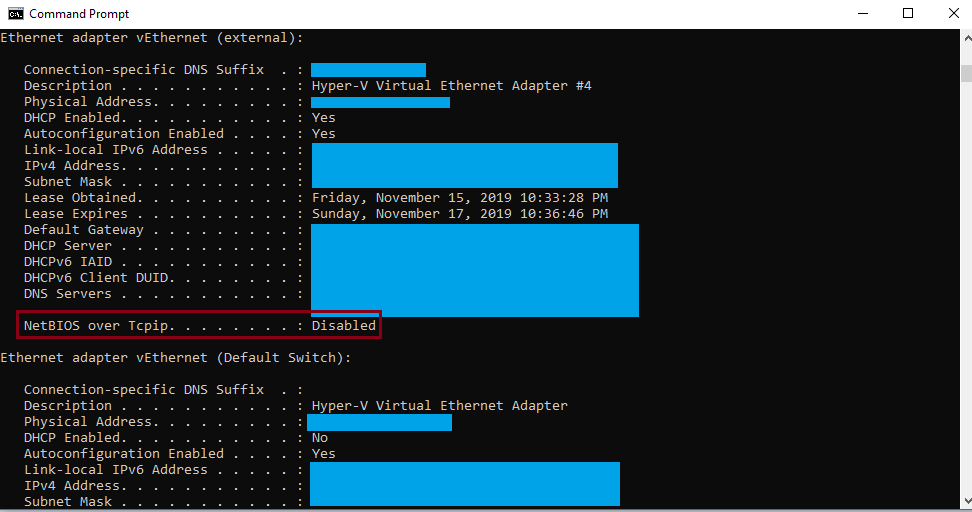
We can locally review if NetBios is disabled typing ipconfig / all on a command prompt window.
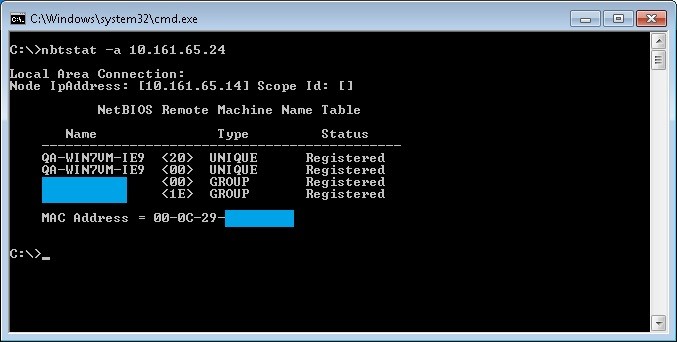
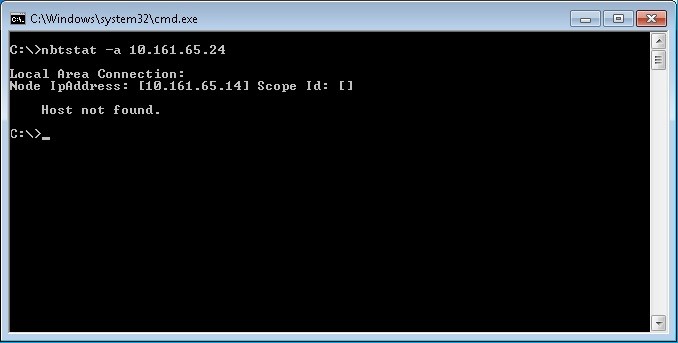
We can also test if a remote system has or not netbios enabled with the following command nbtstat -a “ip address of the remote host to test”, in the example below the system with the ip address 10.161.65.24 has netbios enabled and then we can see the hostname of the remote system
After netbios is disabled on the remote host called QA-WIN7VM-IE9 with the ip address 10.161.65.24, if we run the same command from a system in the same network we should see results like this.
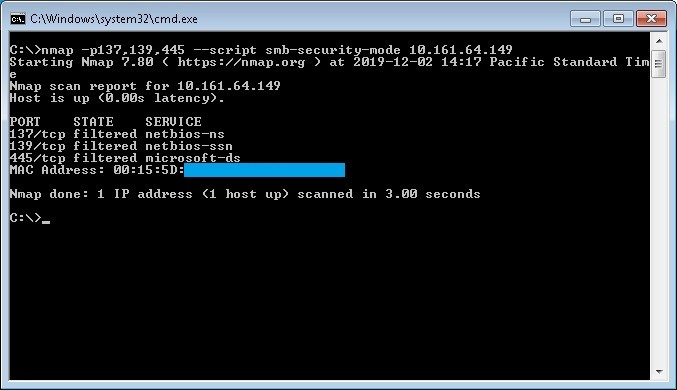
Checking open ports with Nmap tool
With nmap tool we can check for the open ports 137,139,445 with the following command:
nmap -p137,139,445 --script smb-security-mode ip-address
In the following example a port scan has been made for the ip address 10.161.64.149 with the results that ports 139 and 445 are open 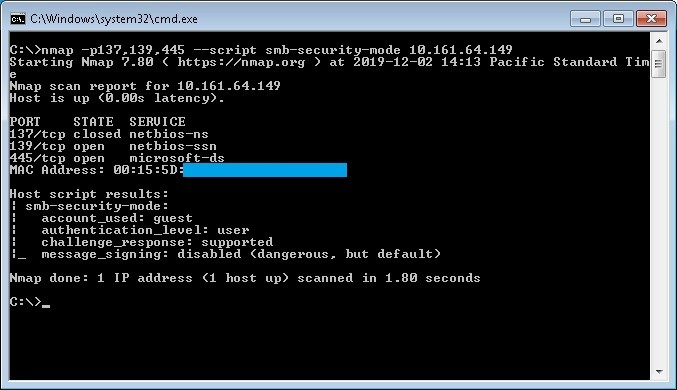
In the following example a port scan has been made for the same ip address after apply firewall rules and/or regedit modification. (Filtered means that a firewall, filter, or other network obstacle is blocking the port so that Nmap cannot tell whether it is open or closed)